Multiscripts
(Excerpt from "The MathML Handbook" by Pavi Sandhu)
Another common type of notation involves objects that have multiple subscripts and superscripts attached to the base expression. This type of notation is used, for example, to represent tensors such as 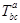 . MathML provides the mmultiscripts element specially for this type of notation. This element can be used to attach any number of vertically aligned pairs of subscripts and superscripts to a base expression. It allows you to attach both prescripts and postscripts notation to the left and right of the base expression, respectively.
. MathML provides the mmultiscripts element specially for this type of notation. This element can be used to attach any number of vertically aligned pairs of subscripts and superscripts to a base expression. It allows you to attach both prescripts and postscripts notation to the left and right of the base expression, respectively.
The syntax for this element is:
<mmultiscripts> base (subscript superscript)* [<mprescripts/> (presubscript presuperscript)*]</mmultiscripts>
The important points to note about the mmultiscripts element are as follows:
- Subscripts are always listed before the corresponding superscript in each subscript-superscript pair.
- If one of the members of a subscript-superscript pair is missing, its position must be explicitly indicated using the empty element none
- The empty element mprescripts must be inserted before you specify any subscript-superscript pairs that occur in the prescript position.
- Prescripts are specified after postscripts since prescripts are relatively uncommon.
- Both prescript and postscript pairs are listed in left-to-right order.
Here is an example:
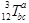
<mmultiscripts>
<mi>T</mi>
<mi>b</mi>
<mi>a</mi>
<mi>c</mi>
<none/>
<mprescripts/>
<mi>1</mi>
<none/>
<mi>2</mi>
<mi>3</mi>
</mmultiscripts>
The mmultiscripts element has two attributes: subscriptshift and superscriptshift. These specify the minimum amount by which a superscript or subscript should be shifted up or down relative to the baseline of the base expression, respectively.
| << back | next >> |
| Tipp der data2type-Redaktion: Zum Thema MathML bieten wir auch folgende Schulungen zur Vertiefung und professionellen Fortbildung an:
|
Copyright © CHARLES RIVER MEDIA, INC., Massachusetts (USA) 2003
Printing of the online version is permitted exclusively for private use. Otherwise this chapter from the book "The MathML Handbook" is subject to the same provisions as those applicable for the hardcover edition: The work including all its components is protected by copyright. All rights reserved, including reproduction, translation, microfilming as well as storage and processing in electronic systems.
CHARLES RIVER MEDIA, INC., 20 Downer Avenue, Suite 3, Hingham, Massachusetts 02043, United States of America








